Ensuring Cable Integrity in Hazardous Areas | Managing challenges & mitigating risks
In industrial settings where explosive atmospheres are a constant concern, the importance of meticulous cable management cannot be overstated. Effective cable management ensures the integrity of electrical systems in major hazard facilities. In this article, we’ll delve into the challenges posed by cable exposure, unsupported cables, and excessive radius bending of cables in hazardous areas, shedding light on the significance of proactive cable management strategies.
Cable Exposure to Harsh Conditions | The sun can threaten cables
In hazardous environments, cables are often exposed to an array of harsh conditions that can degrade their insulation and overall performance. One such threat that might often go unnoticed is the damaging effect of sunlight. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun can lead to the deterioration of cable insulation over time. This not only compromises the electrical integrity of the cable but also increases the risk of water ingress, potentially leading to further electrical faults.
Avoidance of damage according to AS/NZS 60079.14 | Cable systems and accessories should be installed, so far as is practicable, in positions that will prevent them being exposed to mechanical damage, to corrosion or chemical influences (for example solvents), to the effects of heat and to the effects of UV radiation.
To address this concern, it’s crucial to employ cable management solutions that shield cables from direct sunlight exposure. Cable trays (with lids fitted), conduits, and UV-resistant cable coatings are some options to consider. By implementing these measures, organisations can significantly extend the lifespan of cables while minimising the chances of unexpected downtime.


The Perils of Unsupported Cables
Inadequately supported cables can sometimes become dislodged from their intended positions, leaving them in positions susceptible to a range of hazards. One potential risk is the interference with vibrating equipment. Vibrations from machinery can cause cables to rub against sharp edges, adjacent equipment or even other cables and lead to insulation damage. This not only endangers the electrical integrity of the cables but can also result in potentially catastrophic failures.
Adopting effective cable support systems, such as cable tray, conduit and cable ties to support the cables in position can help prevent such occurrences. Regular inspections and maintenance routines are equally vital to ensure that cables remain properly secured and positioned, minimising the chances of unintended contact with equipment. All electrical equipment in hazardous areas should be inspected at least every four years (if not more often).
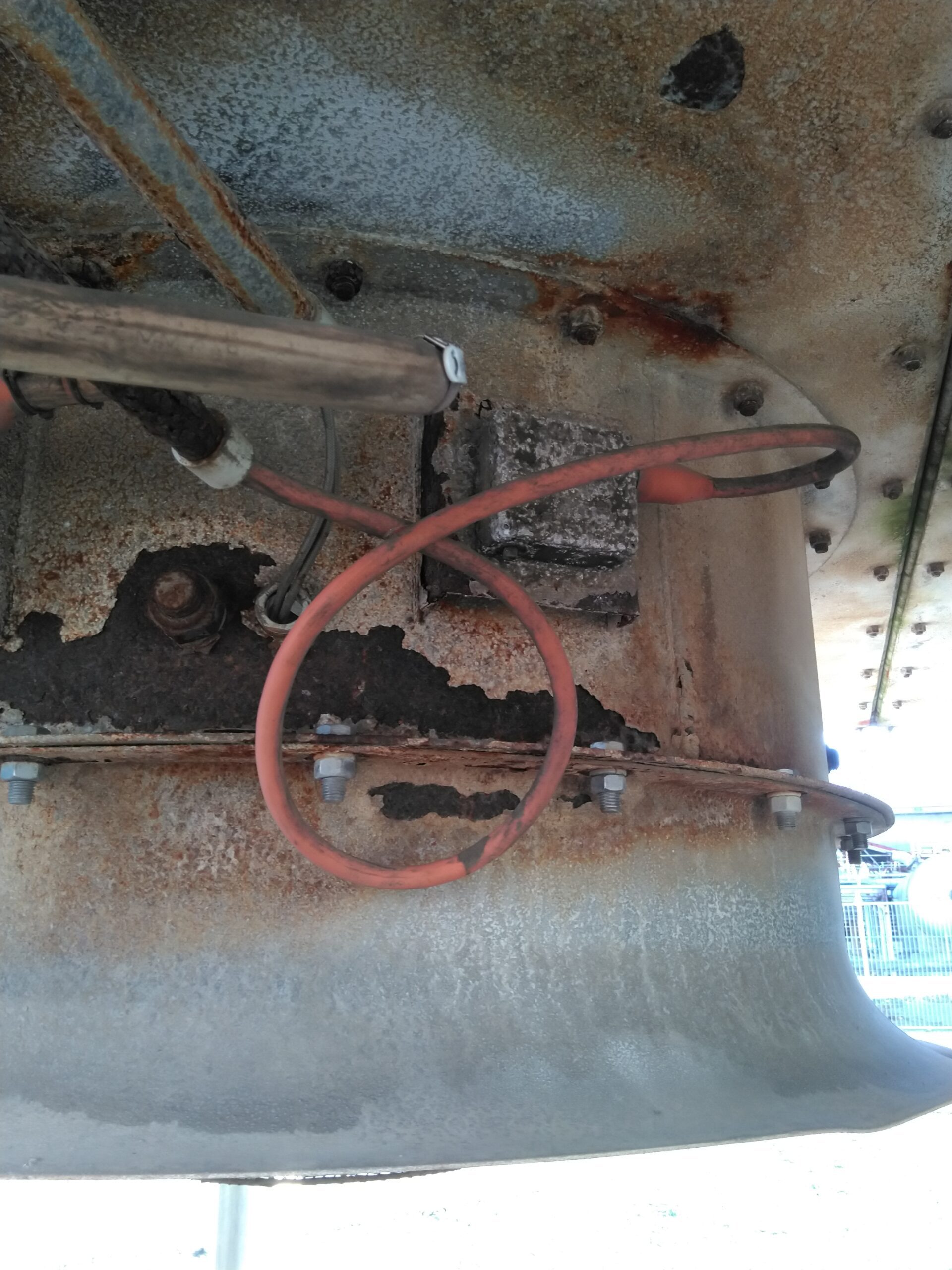
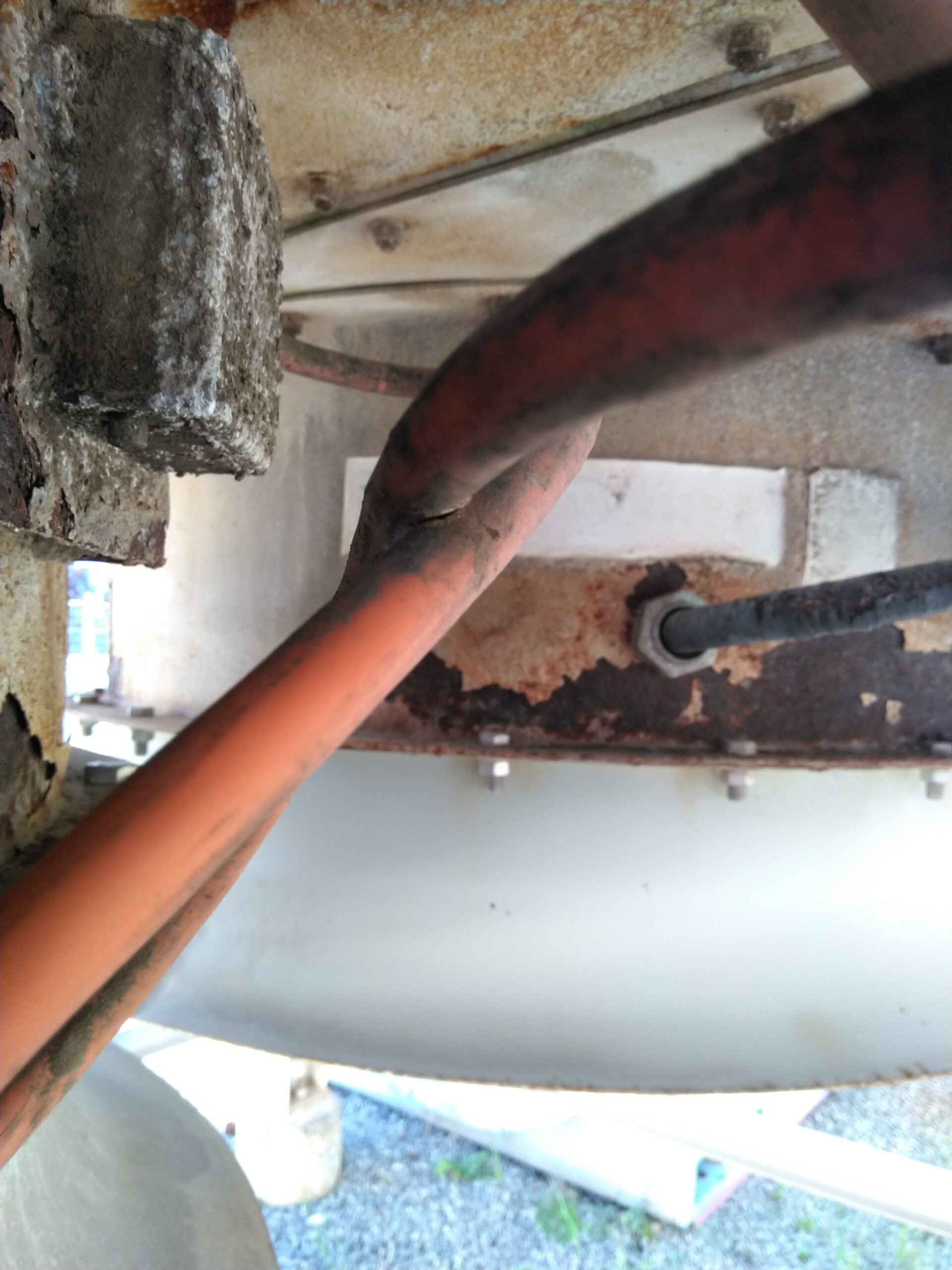



Bending Beyond Limits | Cable Bending Hazards
In hazardous areas, the permissible radial bend of cables is a critical consideration. Excessive bending can lead to insulation breakdown, particularly when an over stretched cable is exposed to the damaging radiation of the sun. Here is Western Australia, the summer temperatures and direct sunlight can cause significant damage to cables over time. Insulation breakdown can expose conductors and increase the likelihood of further cable damage. When cables are bent beyond their designed limits, their capacity to safely conduct electricity is compromised, putting both personnel and equipment at risk.
AS/NZS 60079.14 | Where cables are secured to equipment or cable trays the bend radius on the cable should be in compliance with the cable manufacturer’s data or be at least 8 times the cable diameter to prevent damage to the cable. The bend radius of the cable should start at least 25 mm from the end of the cable gland.
Careful planning during cable installation is essential to prevent bending-related issues. Cable routes should be mapped out, accounting for factors such as necessary bend radii and the potential for dynamic movements. Employing flexible conduit solutions can help facilitate proper cable routing while maintaining necessary safety margins.
Additional Cable support & protection systems of Electrical Equipment in Hazardous Areas
Where even a minor oversight can have far-reaching consequences, the importance of a well-structured cable support systems cannot be emphasised enough. Beyond the challenges mentioned earlier, such as UV exposure and unsupported cables, there are several solutions available that can significantly enhance cable management practices.
Conduit | Mechanical & Environmental Protection
Conduits are a staple in cable management for hazardous areas. Not only does conduit safeguard the cable against mechanical damage but also provide an extra layer of protection against UV protection and chemical spills. When properly selected and installed, conduits shield cables from corrosive substances, moisture, and other environmental hazards prevalent in oil & gas, mining, chemical processing and power generation facilities.
AS/NZS 60079.14 | If required to maintain the appropriate degree of ingress protection (e.g. IP54) of the enclosure, the conduit shall be provided with a conduit sealing device adjacent to the enclosure.
Conduit Sealing Devices | Sealing Ex Equipment
Maintaining the integrity of cable conduits is of paramount importance in hazardous environments. Conduit sealing devices are instrumental in preventing the ingress of hazardous gases, vapours, or dust into conduit systems. These devices effectively create a barrier which isolates cables from the external environment. By employing properly rated conduit sealing solutions, organisations can prevent potential ignition sources and maintain the integrity of the equipment.
The conduit shall be provided with a conduit sealing device where it enters or leaves a hazardous area, to prevent the transmission of gases or liquids from the hazardous areas to
non-hazardous areas. There shall be no union, coupling or other fittings between the sealing device and the hazardous area’s boundary.
Cable Tray | Structured Cable Support
Cable tray is a versatile solution which plays a pivotal role in managing cables in hazardous areas. These trays offer structured pathways for cables, ensuring they remain organised and protected. The open design of cable tray facilitates efficient heat dissipation, preventing the accumulation of heat that could otherwise compromise cable insulation. Moreover, cable trays allow for easy access during installation, maintenance, and inspections, reducing downtime and enhancing overall operational efficiency.
Cable Tray Cover | Shielding against external environmental factors
While cable trays provide exceptional support and organisation, it’s equally important to shield cables from overhead hazards. Cable tray covers provide an additional layer of protection, guarding against falling debris, moisture, and other potential threats. By selecting appropriate covers that adhere to hazardous area regulations, organisations can maintain the structural integrity of cables while minimising risks associated with external factors.
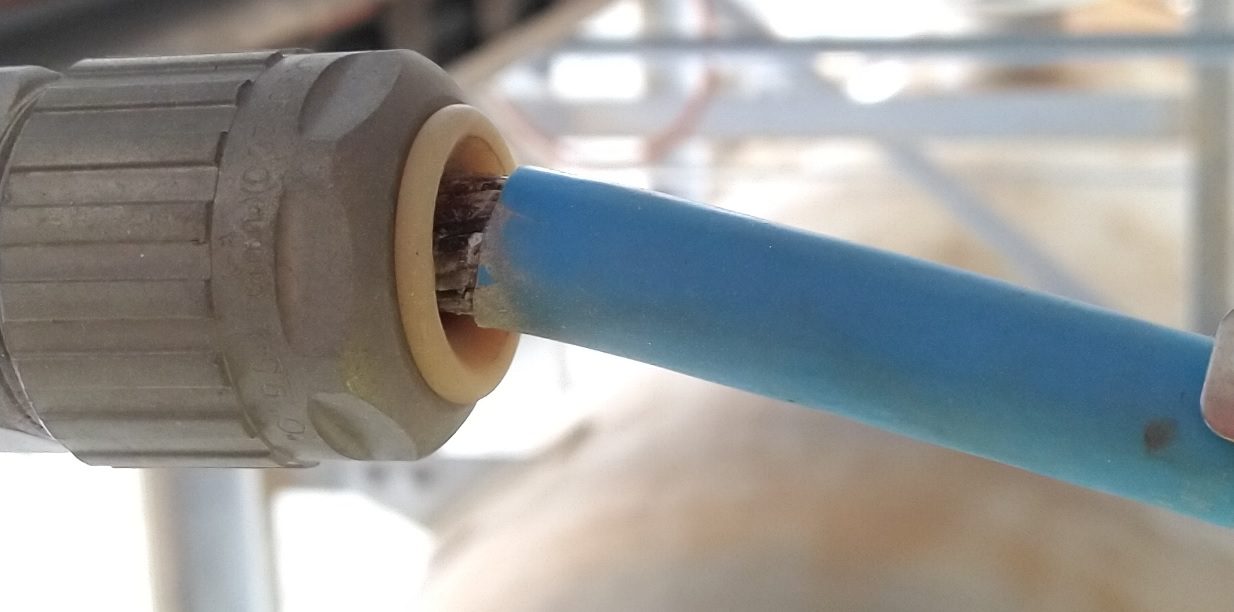
Flexible Conduit | Adapting to Dynamic Environments
In explosive atmospheres where movement and vibrations are commonplace, flexible conduits offer a viable solution. These conduits can accommodate dynamic shifts and vibrations without compromising cable integrity. The flexibility allows cables to move with the equipment or structure they are connected to, reducing stress and abrasion risks. When properly installed, flexible conduits not only enhance safety but also contribute to the longevity of cable systems. Poor installations or maintenance (as in the below pictures), is often a direct cause of cable damage.


Strategic Planning and Collaboration | The Key to Success
Implementing an effective cable support system in hazardous areas demands a holistic approach. Collaborating with experts in cable management, electrical engineering, and safety compliance can provide invaluable insights into selecting the right materials, installation techniques, and maintenance practices. Adhering to relevant standards, such as AS/NZS 60079, ensures that cable support solutions meet stringent safety requirements.
Having a system is no good to anyone, if the system is not implemented and monitored correctly. All EEHA equipment shall be inspected to a detailed grade before it is energised and a close inspection at least every four years (as a minimum).
Conclusion | Safeguarding Cable Systems in Explosive Atmospheres
In conclusion, meticulous cable management in hazardous areas is essential for maintaining the integrity of electrical systems, safeguarding personnel, and preventing catastrophic incidents. By addressing challenges such as UV exposure, unsupported cables, and excessive bending, and by leveraging solutions like conduits, conduit sealing devices, cable trays, and flexible conduits, organisations can establish a comprehensive cable management system. With safety at the forefront, we can navigate the complexities of hazardous areas and explosive atmospheres, promoting operational excellence.
In the pursuit of excellence, it’s imperative to stay updated with industry best practices and evolving standards. Collaborating with experts in hazardous areas and explosive atmospheres, and adhering to relevant regulations, such as the AS/NZS 60079 standard, will contribute to a comprehensive and robust cable management management strategy. Through such measures, we can confidently navigate the intricate terrain of hazardous areas, safeguarding both our assets and our people.

A very important topic! Safety in hazardous locations is paramount, as shown at: https://bit.ly/3l25WWG
Thank you Estellito for your comment. You raise some very interesting arguments in your article. I particularly enjoyed the comments around Exd enclosures and the use of Denso tape. Very interesting!